 Women's World Banking
Women's World Banking
WWB was established in 1979 with the objective of supporting the involvement of women in enterprise creation the world over. It is a non-profit organization.
WWB operates by means of affiliate organizations (over fifty) located in forty countries. It is therefore a network in itself, providing access to financing, information and the market for women micro and small enterpreneurers.
WWB's Goals
- To expand the economic participation of millions of poor women enterpreneurers - through direct services and by influencing government, bank and business policies, practices and paradigms.
- To support local initiatives to build self-sustaining WWB affiliate organizations.
- To create innovative instruments, new relationships and effective systems which give poor women enterpreneurs access to banking services, markets and information.
- To nurture an active, global network of leading enterpreneurers, bankers and community and energy to build businesses and economies with a human face.
- Build networks of enterprises which add value and values - enhance the enterprise of life.
How Women's World Banking Functions
Traditional System Women's World Banking
------------------------ --------------------------
Poor women as passive Poor women as dynamic
beneficiaries economic agents
Social welfare, charity, Sustainable business
paternalism approaches dealing with
economic and social
problems
Local organizations Self-determined local
implementing rojects organizations responding
designed elsewhere to local needs.
Top-down control from Mutual accountability for
outside results at all points
Assistance from outside Lateral learning among
experts practitioners.
Elite versus grassroots Partnerships in banking and
organizations business to change money and
power relationships.
Alternative systems versus Transformational institutions
mainstreaming with major impact.
Relationship Banking

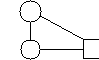 Affiliate-Local Banks-Clients
Affiliate-Local Banks-Clients
- WWB affiliates can leverage their successful experience in direct lending to microenterprise clients and expanding capital bases to negotiate leveraged credit lines with local banks. Affiliates can then use these credit lines to scale-up their micro loan programmes.
This arrangement saatisfies the major needs of the key players in delivering financial services to poor women enterpreneurers.
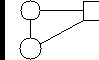 Affiliate-WWB-Local Banks
Affiliate-WWB-Local Banks
- Experience indicates that loan guarantees, in which banks make the loans, work best for small enterprises. For microenterprises, WWB loan guarantees are useful in providing partial guaranteess with affiliates for bank-affiliate-client credit lines. The loan guarantee is not a start-up product. Afiliates need to develop a strong track record first.
In both arrangements, WWB affiliates seek to leverage substantial bank resources for micro- and small enterprise loans.
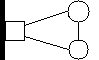 Affiliates-Informal Organizations-Clients
Affiliates-Informal Organizations-Clients
- WWB affiliates are begining to establish themselves as financial intermediaries by on-lending funds to grassroots organizations, rural banks, and women's savings groups.
Many affiliates have access to local and foreign capital and have financial management know-how. Informal organizations have clients in areas not yet reached by WWB affiliates. By combining these advantages, WWB affilites can reach greater numbers of poor women enterpreneurers.
 Affiliates-WWB-Funding Partners
Affiliates-WWB-Funding Partners
- Fnding partners are recongizing that one of the most strategic means of funding with a strong track record is through affiliate capitalization.
With a strong track record, a sound business plan, and network inputs specified under the WWB Affiliate-Network Partnership Agreement, affiliate capital funds can be used to build self-sustaining institutions. Capitlization enables affiliates to: generate income to cover core operating costs, expand direct lending, and leverage substantial local resources.
- Source:
- Abstracted from Vincent, Fernand, "Alternative Financing of Third World ORganizations and NGOs" Volume I, IRED-CTA-FGC-RAFAD. 1995.
Return to

Women's World Banking
Hari Srinivas - hsrinivas@gdrc.org
 Return to the Virtual Library on Microcredit
Return to the Virtual Library on Microcredit

 Women's World Banking
Women's World Banking
 Affiliate-Local Banks-Clients
Affiliate-Local Banks-Clients
 Affiliate-WWB-Local Banks
Affiliate-WWB-Local Banks
 Affiliates-Informal Organizations-Clients
Affiliates-Informal Organizations-Clients
 Affiliates-WWB-Funding Partners
Affiliates-WWB-Funding Partners

 Return to the Virtual Library on Microcredit
Return to the Virtual Library on Microcredit