Climate Change
This section provides a framework for understanding the Post 2015 Development Agendas.
When the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) ended in 2015, the international community came together once again, under the auspices of the United Nations, to formulate a development agenda for adoption beyond 2015.
These six agendas (which go beyond just the SDGs) together became known as the "Post-2015 Agendas"
The Climate Change Agenda demands urgent global cooperation to drastically reduce emissions, strengthen adaptation, and mobilize finance to limit global warming and protect vulnerable communities. It calls for transformative action in energy, industry, transport, and ecosystems to secure a sustainable future.

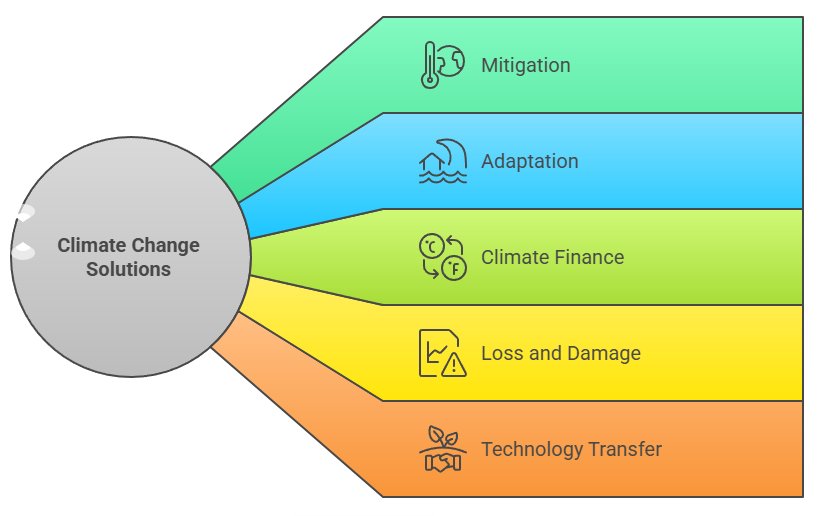
Main Thematic Areas:
- Mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions
- Adaptation and resilience
- Climate finance
- Loss and damage
- Technology transfer
Pathways to Climate Change Solutions
Facts and Figures:
- 2023 was the hottest year on record, with global temperatures 1.48<C above pre-industrial levels (WMO, 2024).
- Only about $83 billion was mobilized towards the $100 billion annual climate finance goal by 2020 (OECD).
- The Paris Agreement's goal is to limit global warming to well below 2<C.
- Coastal flooding could displace up to 410 million people by 2100 if emissions remain high (Nature Climate Change, 2021).
- Renewable energy now accounts for about 29% of global electricity generation (IRENA, 2023).
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC): Established in 1992, the UNFCCC provides the foundational legal framework for international efforts to tackle climate change through negotiations and binding commitments.
- Paris Agreement: Adopted in 2015, this landmark agreement aims to limit global warming to well below 2<C and pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5<C, while enhancing countries' adaptive capacities and financial support.
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): Each country outlines its individual climate action plan under the Paris Agreement through NDCs, which are reviewed and updated every five years to increase ambition.
- COP (Conference of the Parties) Meetings: Annual gatherings of the 198 Parties to the UNFCCC where negotiations take place, progress is assessed, and further measures are adopted to advance global climate action.
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
- Paris Agreement
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- COP (Conference of the Parties) Meetings
UN Focal Agency:
Case Studies| 350.org (Global): 350.org organizes grassroots campaigns to divest from fossil fuels and accelerate the transition to renewable energy, focusing on climate mitigation aligned with the Paris Agreement goals. | Climate Action Network (CAN) International (Global): CAN supports over 1,500 NGOs in coordinating advocacy at UNFCCC meetings and pushing for ambitious Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) from governments. | Indigenous Environmental Network (Americas): This network empowers indigenous communities to advocate for climate justice and protect traditional lands against deforestation and extractive industries, linking local struggles to global climate debates. |
| Green Climate Fund (Global): The GCF finances climate mitigation and adaptation projects in developing countries, including renewable energy installations and resilient agriculture initiatives aligned with the Paris Agreement. | Barefoot College (India): This grassroots organization trains rural women, including grandmothers, to become solar engineers, spreading off-grid renewable energy to remote areas while promoting climate resilience. | M angrove Restoration in Senegal (West Africa): Local communities have restored thousands of hectares of mangrove forests to capture carbon, protect coastal zones, and sustain fishery-based livelihoods. |
GDRC Research Output |
| ||||||||||||||||