Habitat Agenda
This section provides a framework for understanding the Post 2015 Development Agendas.
When the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) ended in 2015, the international community came together once again, under the auspices of the United Nations, to formulate a development agenda for adoption beyond 2015.
These six agendas (which go beyond just the SDGs) together became known as the "Post-2015 Agendas"
The Habitat Agenda advocates for sustainable urbanization by promoting adequate shelter, inclusive cities, and environmentally sound infrastructure for all. It calls for rights-based, participatory, and resilient approaches to managing urban growth and reducing inequalities in human settlements.

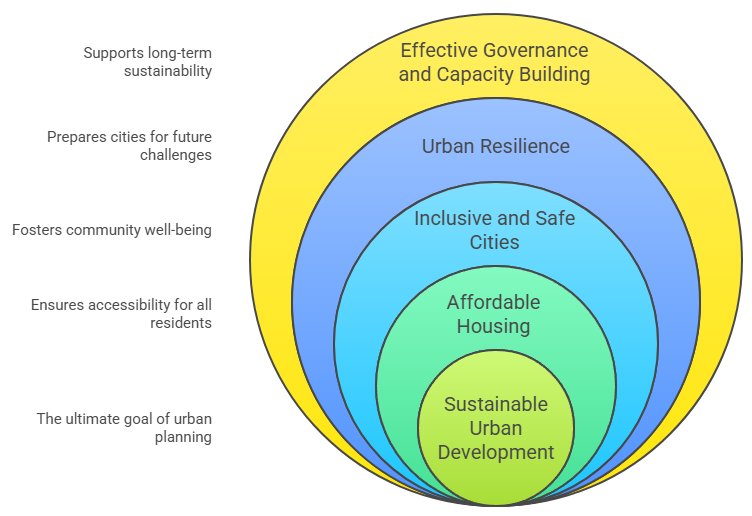
Main Thematic Areas:
- Sustainable urban development
- Affordable housing
- Inclusive and safe cities
- Urban resilience
- Governance and local capacity building
Sustainable Urban Development
Facts and Figures:
- By 2050, 68% of the world population will live in urban areas (UN DESA, 2023).
- About 1.6 billion people lack adequate housing worldwide.
- Urban areas are responsible for about 70% of global CO2 emissions (UN-Habitat).
- Only 38% of countries have national urban policies (UN-Habitat, 2022).
- The New Urban Agenda calls for cities that are inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
- New Urban Agenda: Adopted at the Habitat III Conference in 2016, this framework guides sustainable urbanization over the next two decades, focusing on inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable cities.
- World Urban Forum: A non-legislative technical forum convened by UN-Habitat, held every two years to debate emerging urban challenges and promote the implementation of the New Urban Agenda.
- National Urban Policies (NUPs): Countries are encouraged to formulate and implement national urban policies as strategic frameworks to guide sustainable urban growth, improve city governance, and reduce inequalities.
- New Urban Agenda
- World Urban Forum
- National Urban Policies (NUPs)
Case Studies
| Slum Dwellers International (SDI) (Global South): SDI supports urban poor communities in organizing themselves to negotiate with city authorities for land tenure, improved housing, and basic services. | Habitat for Humanity (Global): Habitat for Humanity builds affordable housing and supports community-driven urban upgrading initiatives to promote inclusive, resilient urban environments. | Shack/Slum Dwellers International (SDI) - India Chapter (SPARC): SPARC partners with local federations of the urban poor to develop participatory slum redevelopment projects in line with the New Urban Agenda. |
| K igali Urban Transport Improvement (Rwanda): The project introduces bus rapid transit systems, pedestrian infrastructure, and urban green spaces to support inclusive and low-carbon urban growth. | P articipatory Slum Upgrading Programme (Africa, Caribbean, and Pacific): Led by UN-Habitat, this initiative promotes community planning and basic service provision in informal settlements. | C 40 Cities (Global): This network of nearly 100 cities implements urban climate action plans, focusing on green infrastructure, public transport, and clean air to create sustainable urban environments. |
GDRC Research Output |
|