Finance for Development
This section provides a framework for understanding the Post 2015 Development Agendas.
When the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) ended in 2015, the international community came together once again, under the auspices of the United Nations, to formulate a development agenda for adoption beyond 2015.
These six agendas (which go beyond just the SDGs) together became known as the "Post-2015 Agendas"
Finance for Development emphasizes mobilizing sufficient and sustainable financial resources at all levels to support inclusive and resilient development. It underlines the need for systemic reforms in taxation, debt management, trade, and investment to close the funding gap for sustainable goals.

Main Thematic Areas:
- Mobilization of domestic resources
- International development cooperation
- Private sector engagement
- Debt sustainability
- Trade as an engine for development
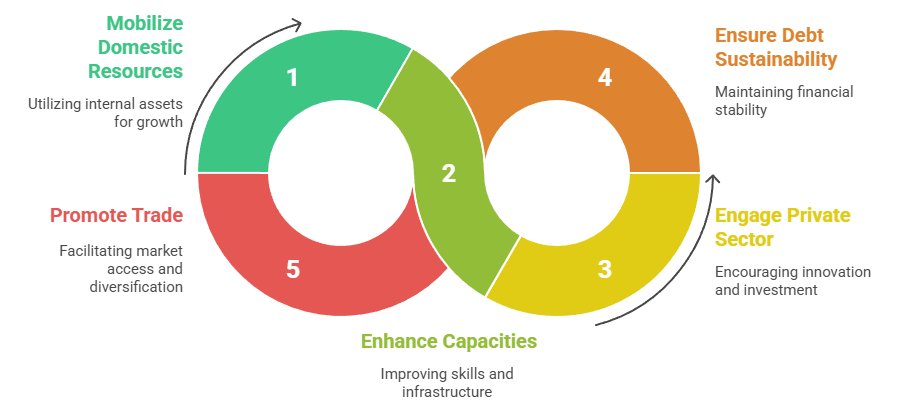
Cycle of Sustainable Economic Development
Facts and Figures:
- Global tax evasion costs developing countries around $200 billion annually (Global Financial Integrity, 2021).
- The Addis Ababa Action Agenda (2015) serves as the foundation for FfD.
- Official Development Assistance (ODA) reached $211 billion in 2022, a record high (OECD).
- Developing countries' external debt reached $11.5 trillion in 2023 (World Bank).
- Remittances to low- and middle-income countries were about $656 billion in 2023 (World Bank).
- Addis Ababa Action Agenda: Adopted at the Third International Conference on Financing for Development in 2015, this agreement sets out a comprehensive set of policy actions to finance sustainable development.
- Financing for Development Forums: Annual intergovernmental forums held at the UN to monitor and discuss the implementation of the Addis Agenda and to explore emerging issues in development finance.
- Inter-agency Task Force on Financing for Development: A collaborative UN initiative that produces annual reports assessing global progress on financing sustainable development, offering policy advice and coordination.
- Addis Ababa Action Agenda
- Financing for Development Forums
- Inter-agency Task Force on Financing for Development
| Eurodad (Europe): The European Network on Debt and Development campaigns for fair and transparent financial systems, including efforts to reform tax rules and advocate for debt relief for developing countries. | Tax Justice Network (Global): This NGO highlights global tax abuses and lobbies for international tax reforms to prevent illicit financial flows that drain resources away from sustainable development. | Jubilee USA Network (USA and Global South): Focused on financial inclusion and debt cancellation, Jubilee USA works with religious groups and development NGOs to push for fair lending practices and responsible finance. |
| Innovative Finance Foundation (Switzerland): Through tools like air-ticket solidarity levies, the foundation supports sustainable health and education financing, aligning with FfD principles and SDG 17. | African Risk Capacity (Africa): This insurance mechanism helps African governments respond quickly to climate shocks like droughts, improving fiscal resilience and protecting development investments. | Philippine Public?Private Partnership Center (Philippines): The PPP Center facilitates infrastructure financing through private investment in transport, water, and social services, contributing to FfD and SDG implementation. |
GDRC Research Output |
|